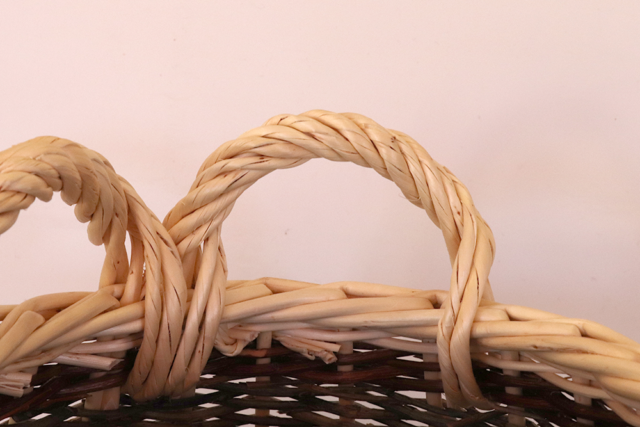
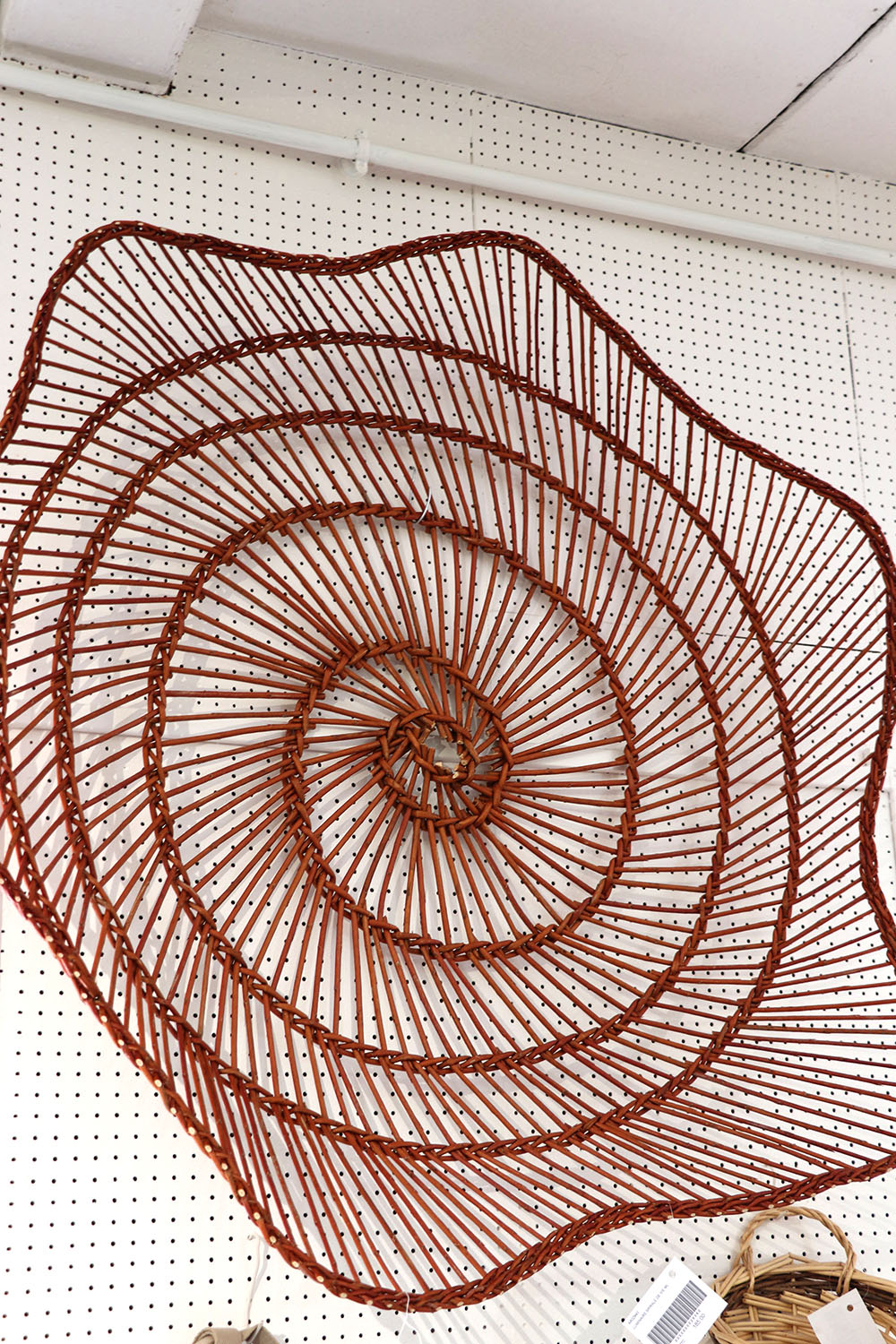
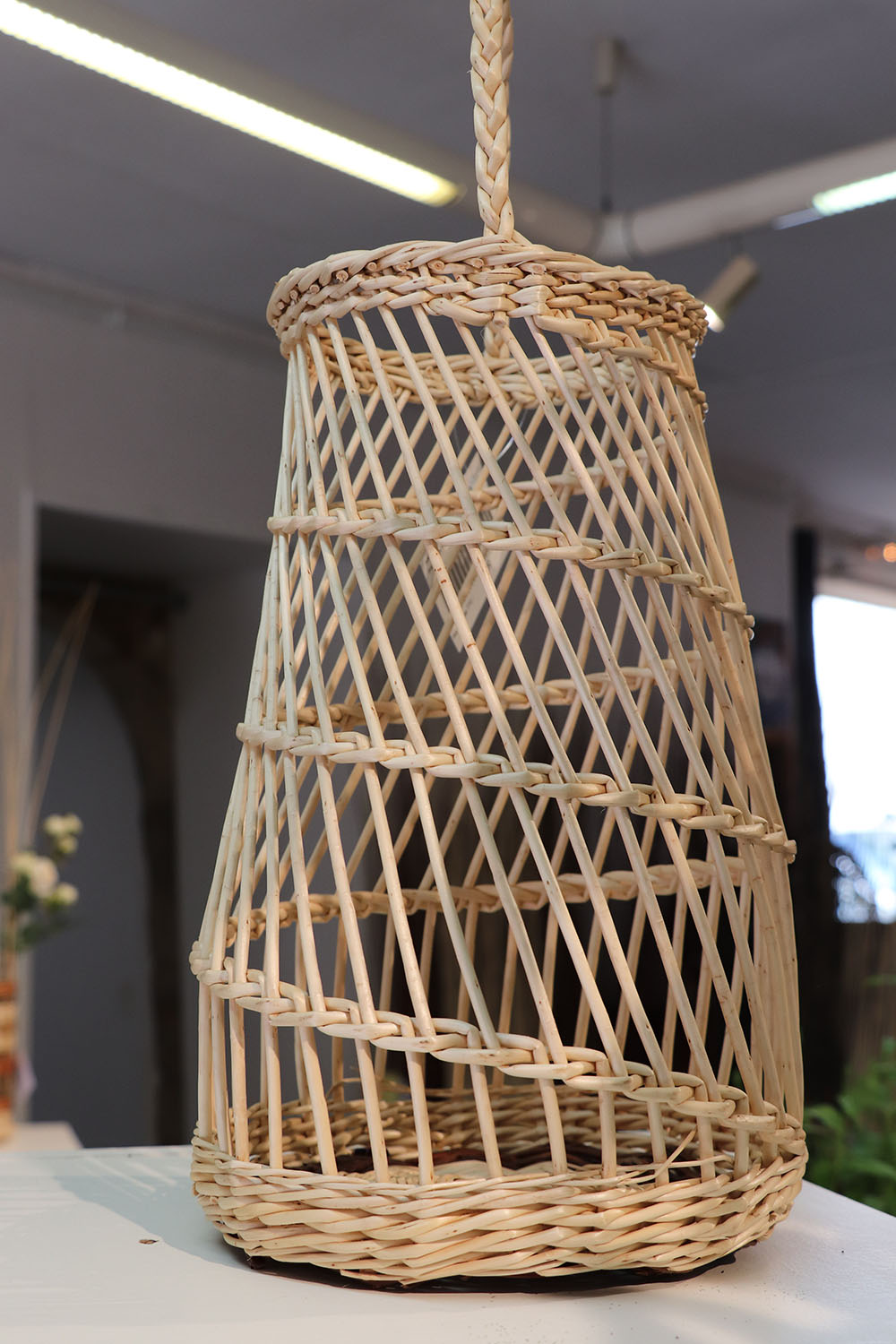
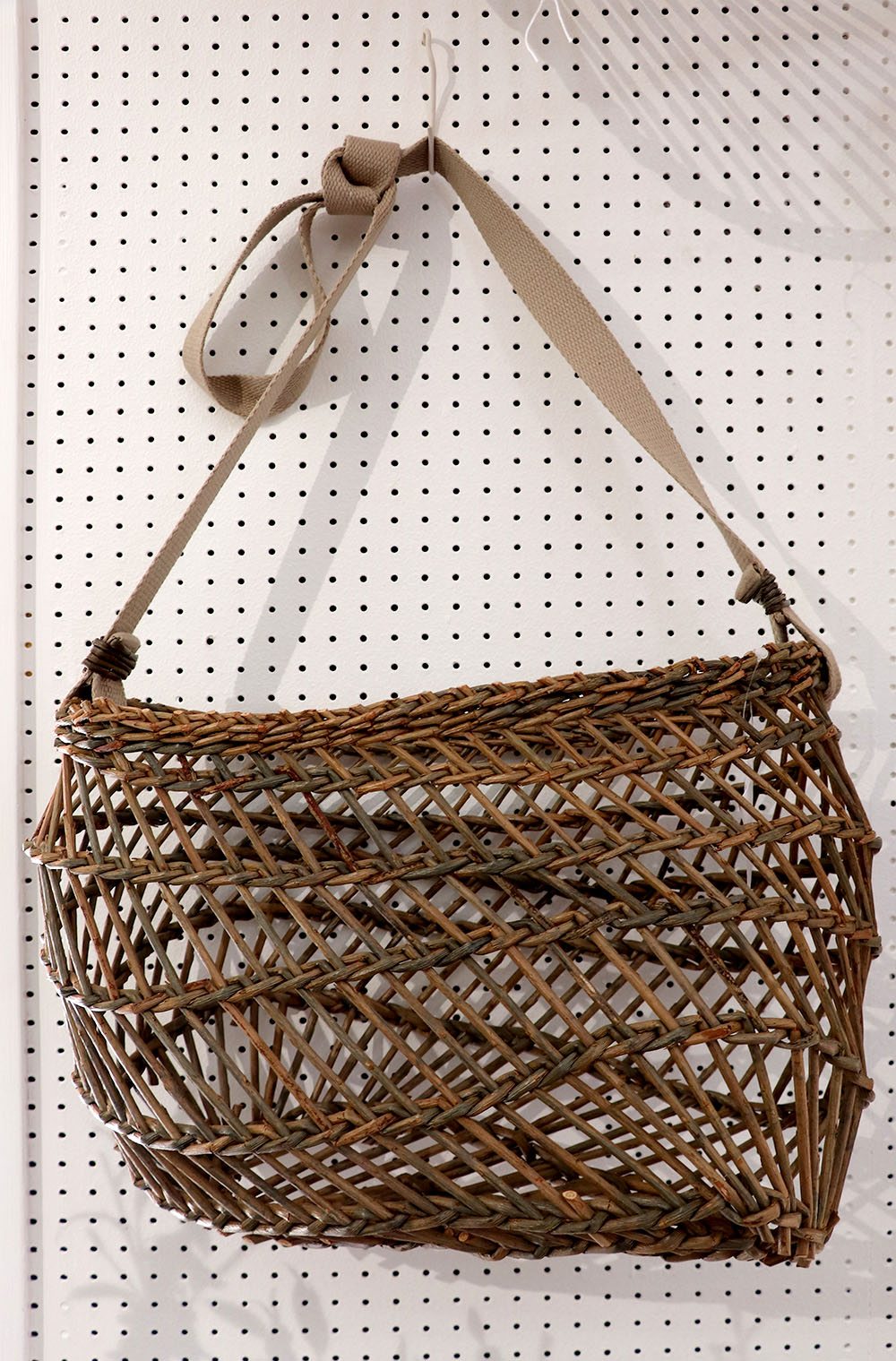
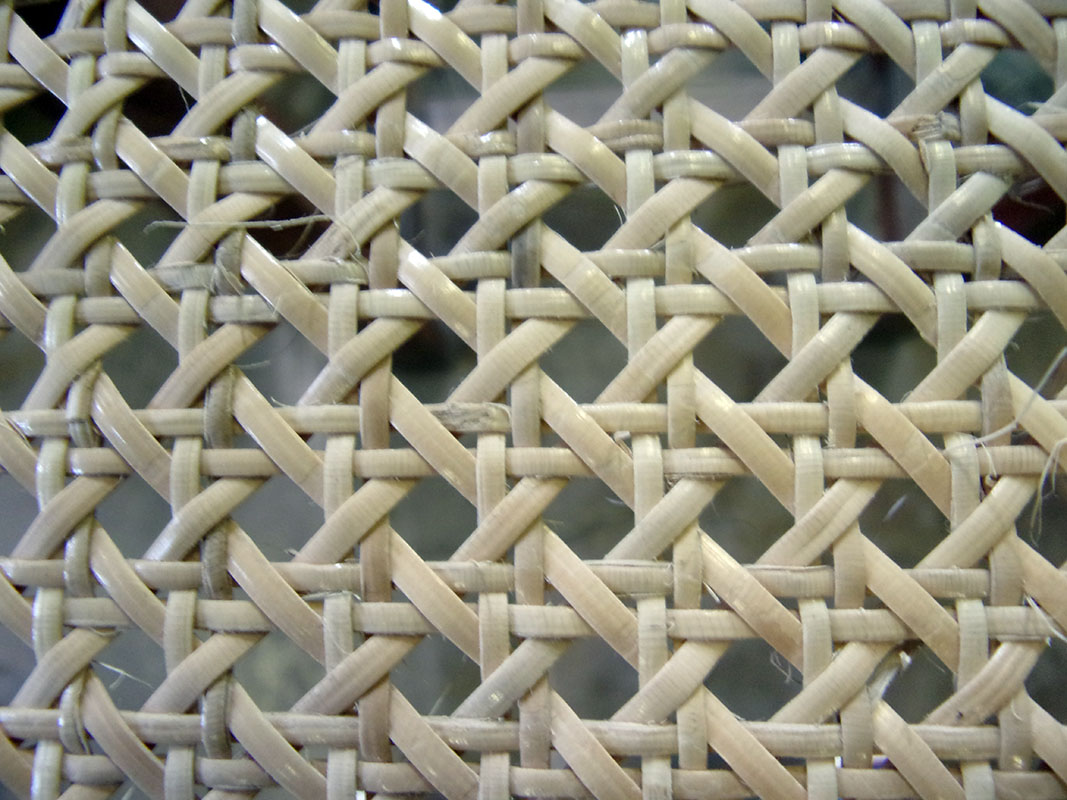
Cove
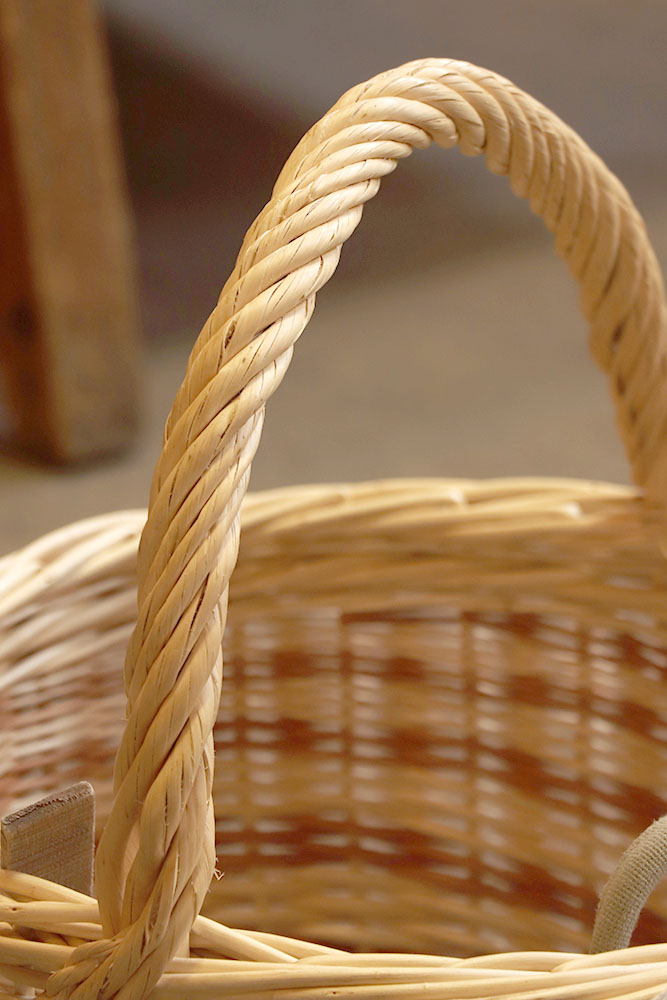
The curved part of the basket, either arched, semicircular or ring-shaped, through which certain containers are picked up. There are small coves (or handles) for carrying the basket with two hands and large coves for carrying the basket with one hand.
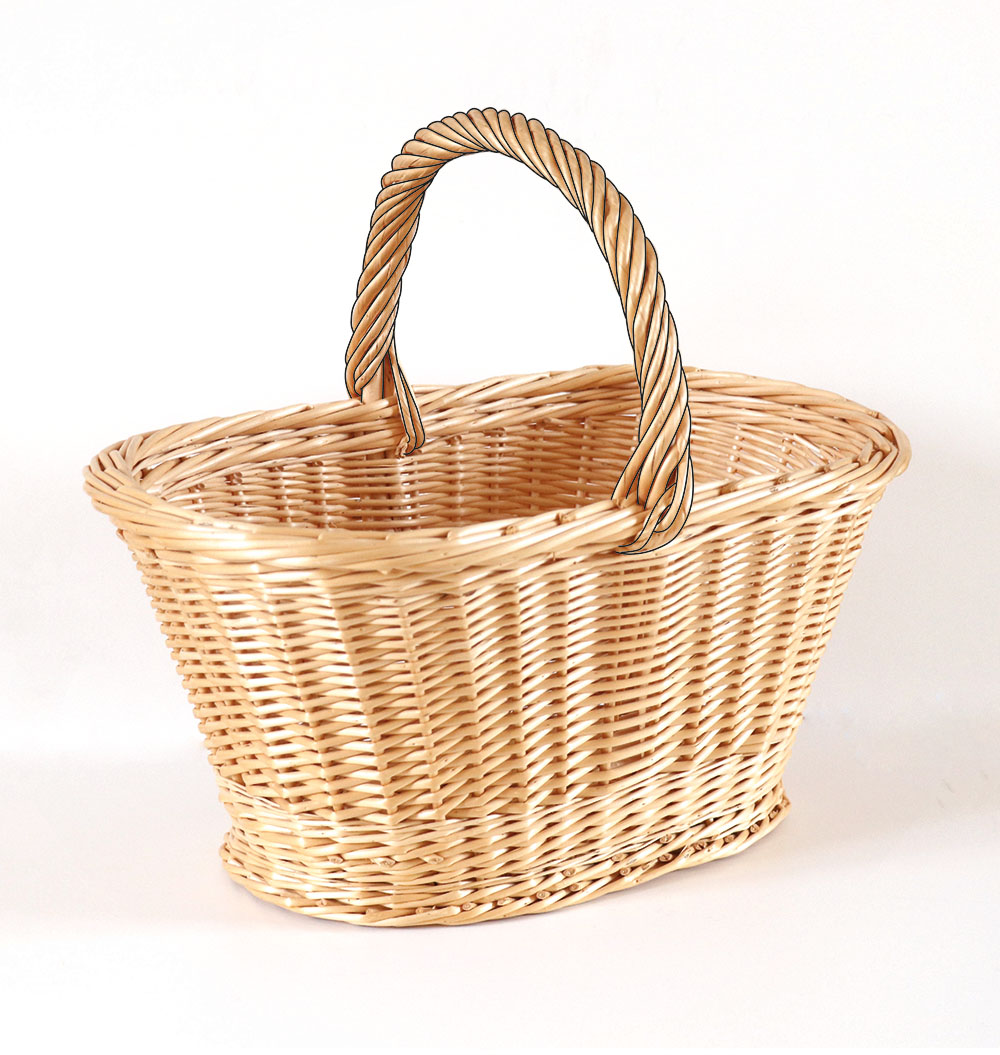


Splinted cove
Used for light baskets, it consists of a sub-cove surrounded by a thin splint of regular width.
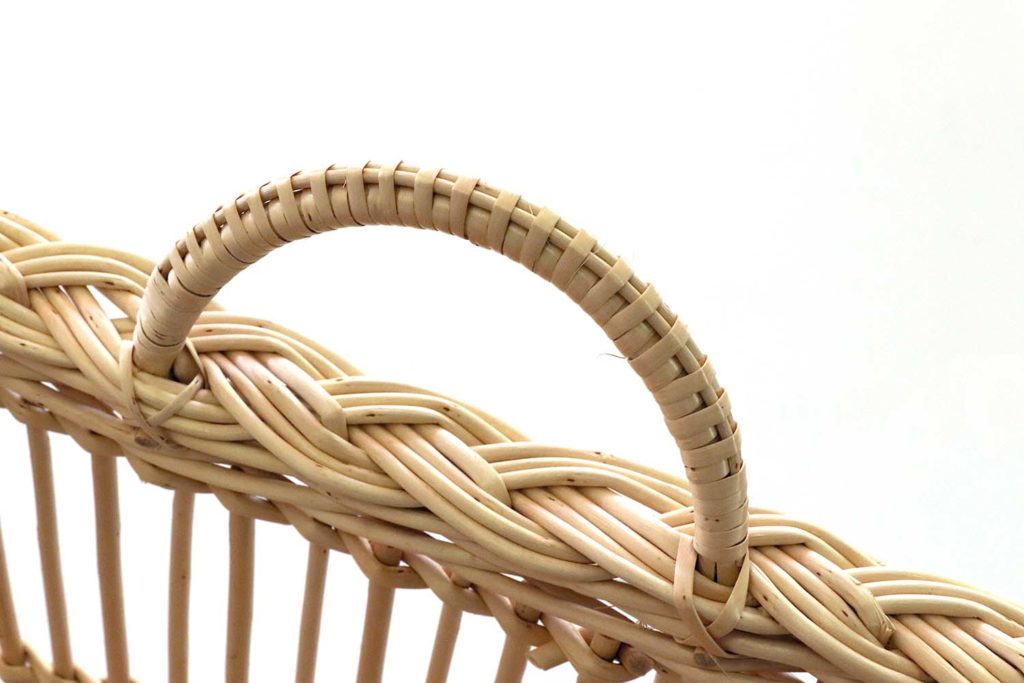



Large wickerwork item
Traditionally utilitarian article, robust and intended for very frequent use, often adapted to a specific trade (bakery, laundry, agriculture, etc.)

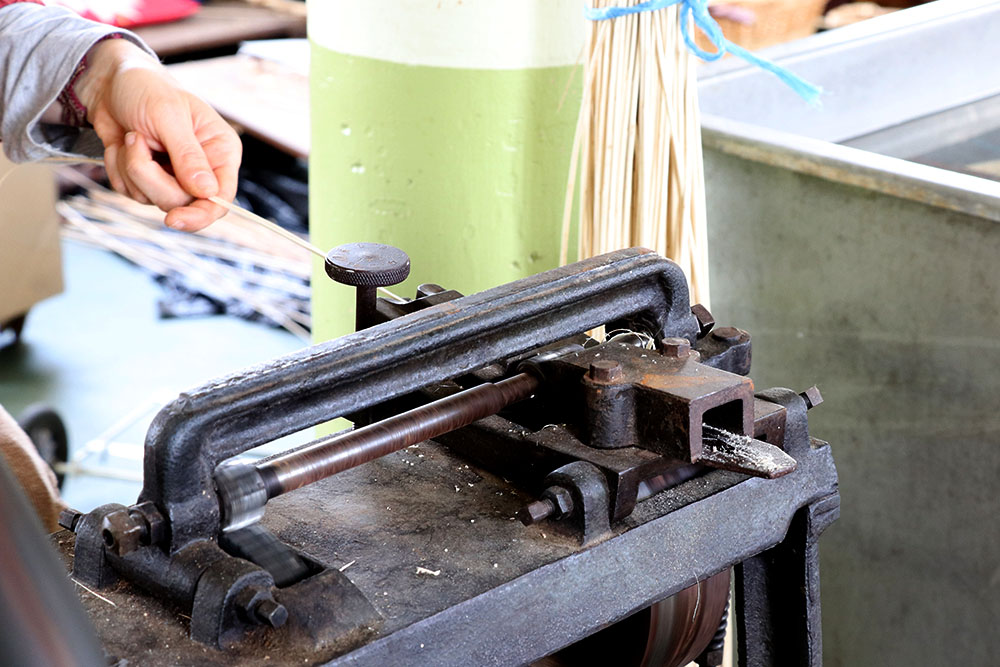
Bat
A piece of iron used to compact the weaving of the wicker strands as they are made. It is fitted with a ring to straighten the large wicker strands.



Socket edge
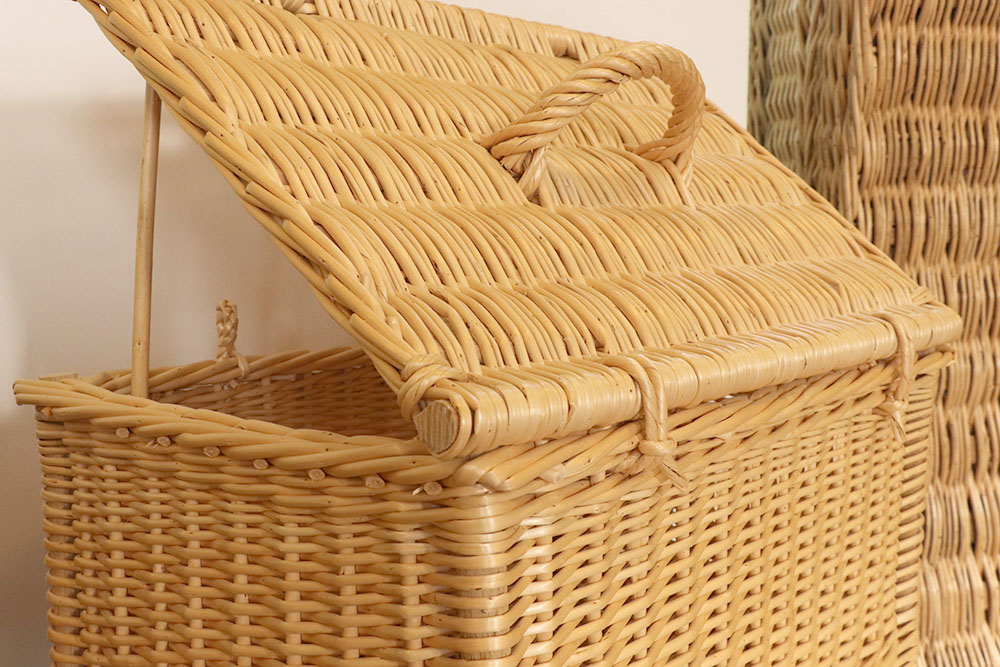
Mainly used at the edge of baskets with interlocking lids. A distinction must therefore be made between the basket and the lid fitting.

Edge
Technique that finishes the object. The border is made with the ribs which are layered and braided in various ways.

Twined weaving
Weaving with a single strand that is weaved along its entire length. Once the strand has been weaved, we continue to weave with a new strand, in front of and than behind the reinforcing strands.

Strand followed weaving
The strands are laid and worked one by one, with the next one laid in the gap just to the right of the first. This overlap creates a visual spiral effect around the perimeter of the item.

English openwork wicker
Openwork wicker often used between two strips of weaving to enhance the work.

Openwork wicker
Openwork in which the ribs cross the coursons between two traces. The ribs are not in the same trace passage unlike the double openwork.

Crocane weaving
This weaving gives a very regular appearance to the work in which one strand is placed behind each ribs ; there are therefore as many strands as there are ribs, all of the same length, which start and end at the same time.

Double crocane weaving
Clôture en crocane dans laquelle deux brins sont placés derrière chaque montant (ici les montants sont également doublés, ce n’est pas forcément le cas).

Damask weaving
Strand followed weaving in which the strands are very tightly packed with a bat until the ribs are completely hidden (formerly used to make fire buckets to carry water).

Swiss leg weaving
Crocane weaving in which every second strand is made of raw wicker. This alternation of colours creates a pattern.

Chain pairing
A weaving with two strands that pass in turn over one rib and then under the other. Once the strands have been weaved, it continues with new strands. This type of weaving is generally used to make basket' bottoms.

Little torch weaving
Crocane weaving with a passageway of two in front of the ribs and one behind them.


Zigzag weaving
A two-strand weaving that is weaved on two diagonal ribs. The entire height is weaved. Then repeat the operation so that the strands cross each other on one of the ribs.

Corner
Large diameter turned wooden ribs, placed in the corners of a rectangular basket or a wood basket for example.


Hulling
Also known as peeling or debarking, this is the action of removing the bark from the wicker to obtain white wicker. Formerly done manually, it is now done mechanically using a huller.

Chipping away
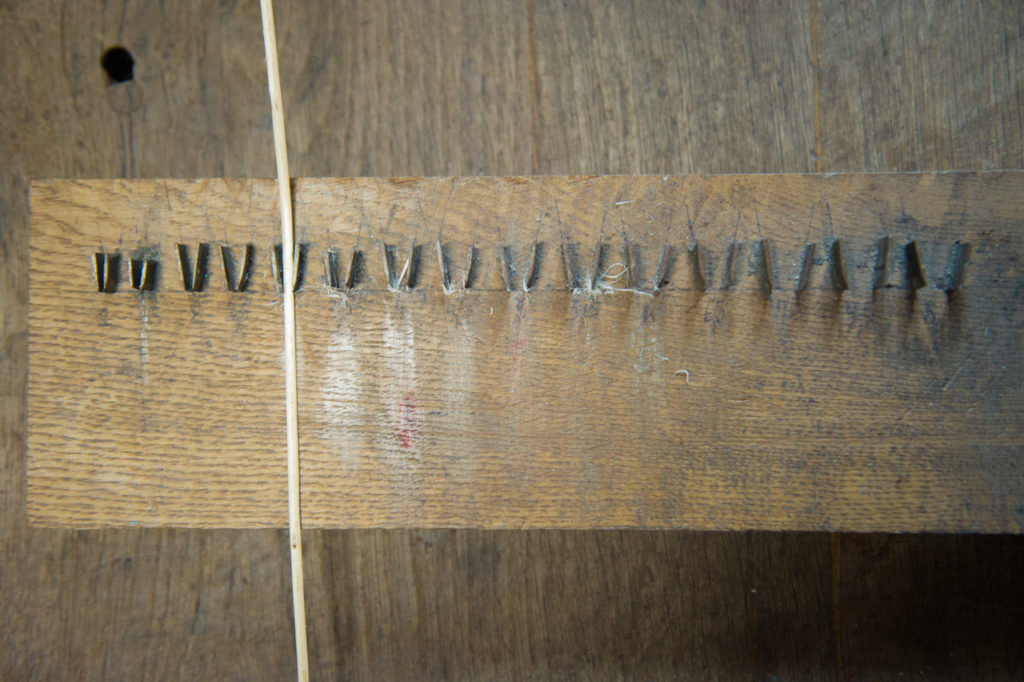
Thin the strand that will act as the rib on part of the foot, so that it is flat and flexible enough to turn around the large strand (the core) that forms the framework (or mould) of the bottom. Scaled strands are called "Chipped away".
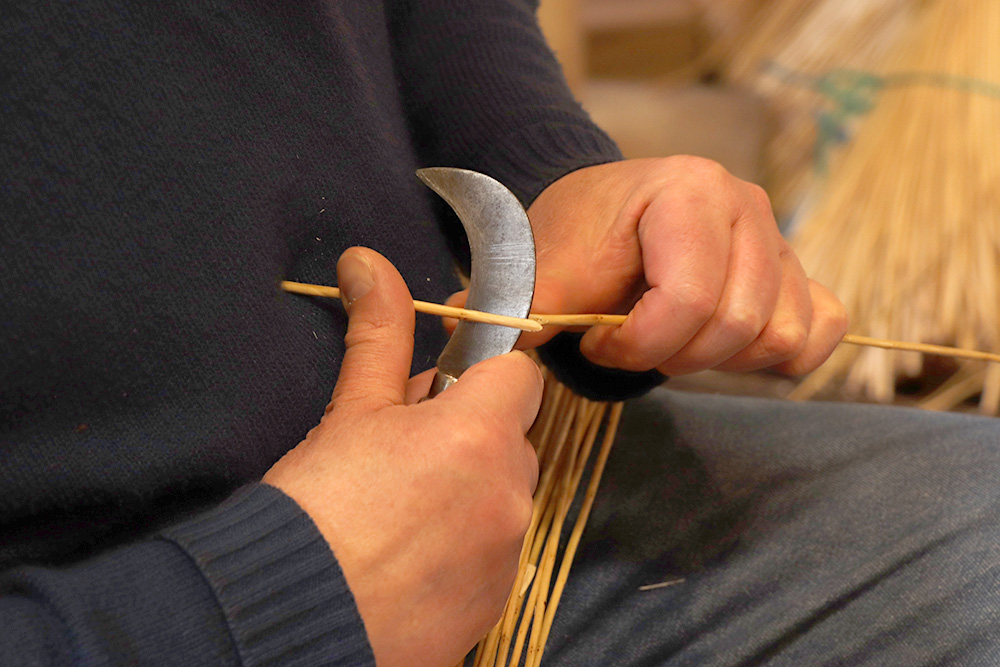
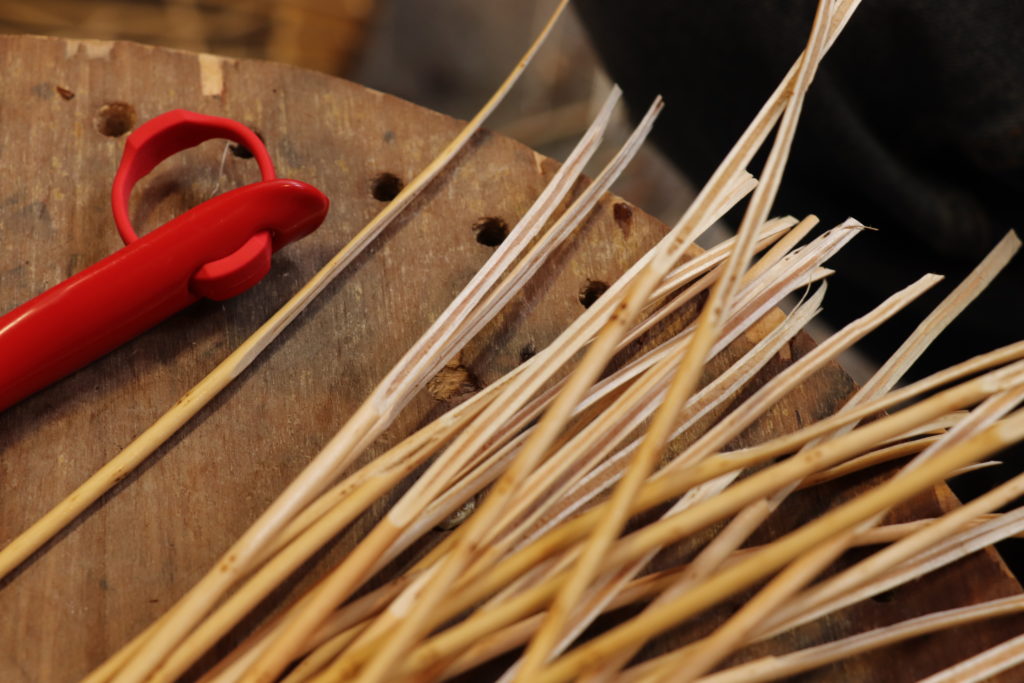



Wicker splint
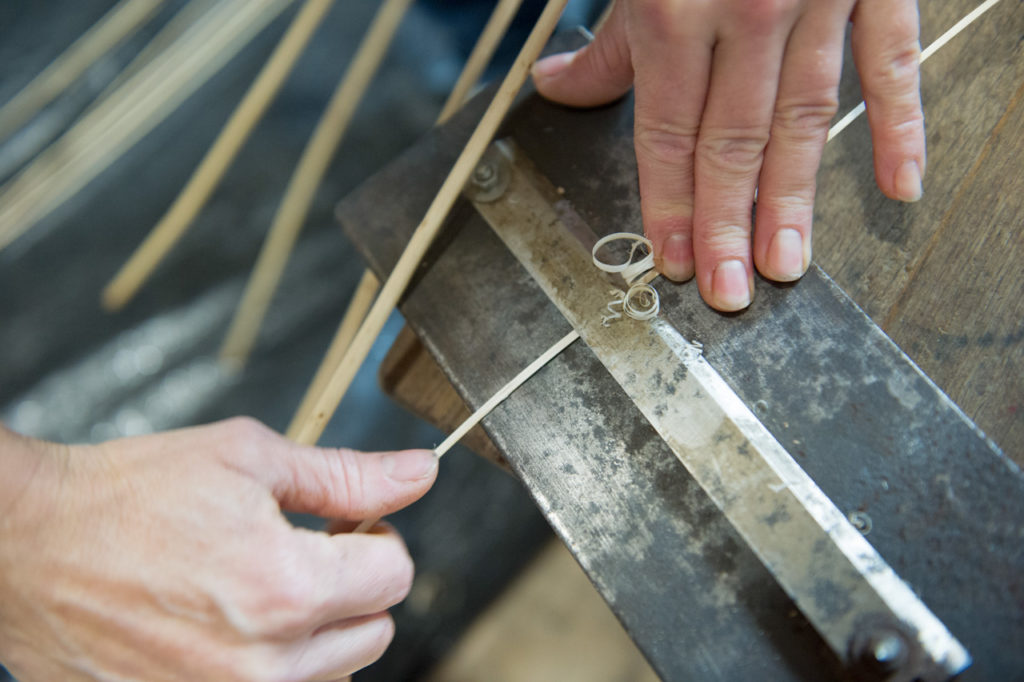
A thin and regular strip of wicker that is calibrated in width and thickness. Made by hand with the help of a scratch gauge or mechanically with a splicing machine.

Rattan bark splint
A thin, regular slat obtained by passing the rattan stem with its bark through a splitting machine. Smooth, shiny and darker than rattan marrow or wicker splint.

Rattan marrow splint
A thin, even strip obtained by running the rattan marrow through a splitting machine.

Peeling
At the end of the weaving process, cut off any excess strand ends on the inside or outside of the article with a pair of secateurs or a peeler.

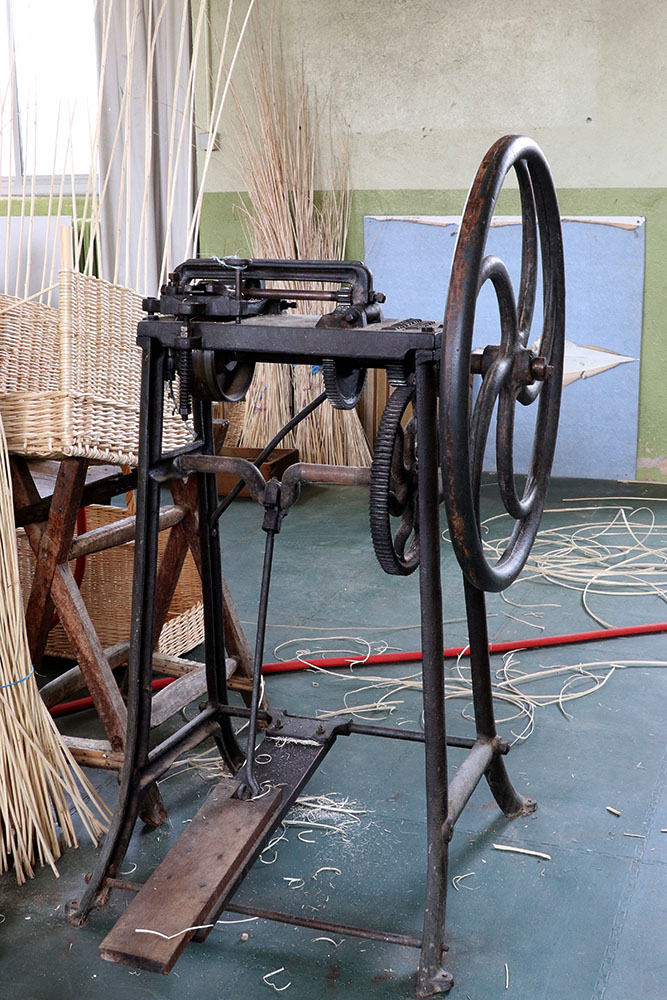
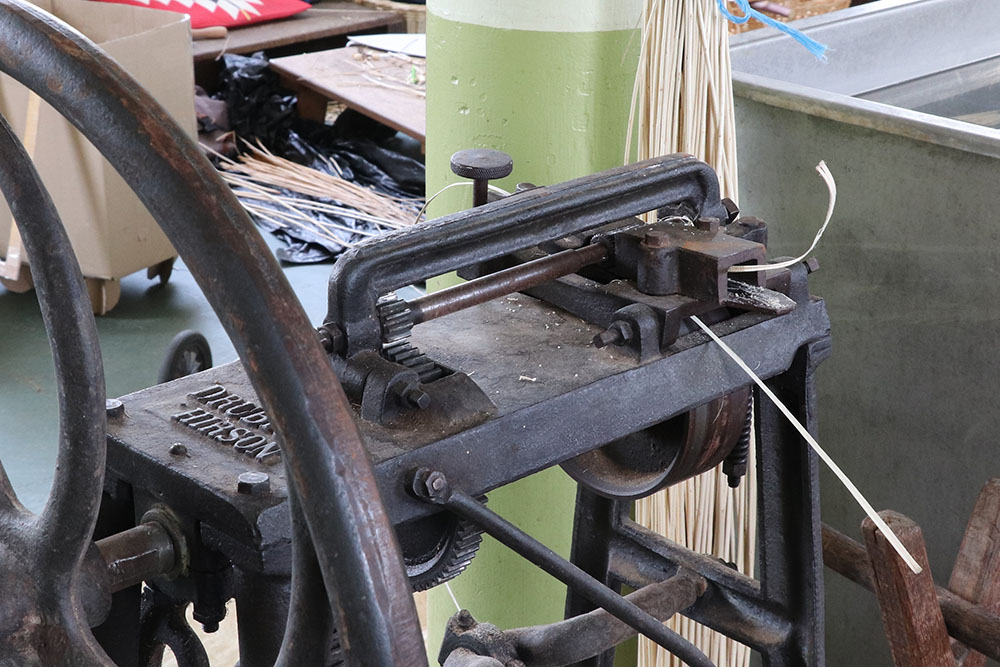
Splitting machine
Machine pour fendre l’osier mécaniquement. L’osier est fendu avant la fabrication d’éclisses.

Splitter
A tool for splitting wicker by hand. A pear-shaped piece of hardwood with a fin at the end. The wicker is split prior to the manufacture of splints.



Closure
Also called nose and crunched-nose A system consisting of two elements that allow the lid to be kept closed on the basket for transport, for example.

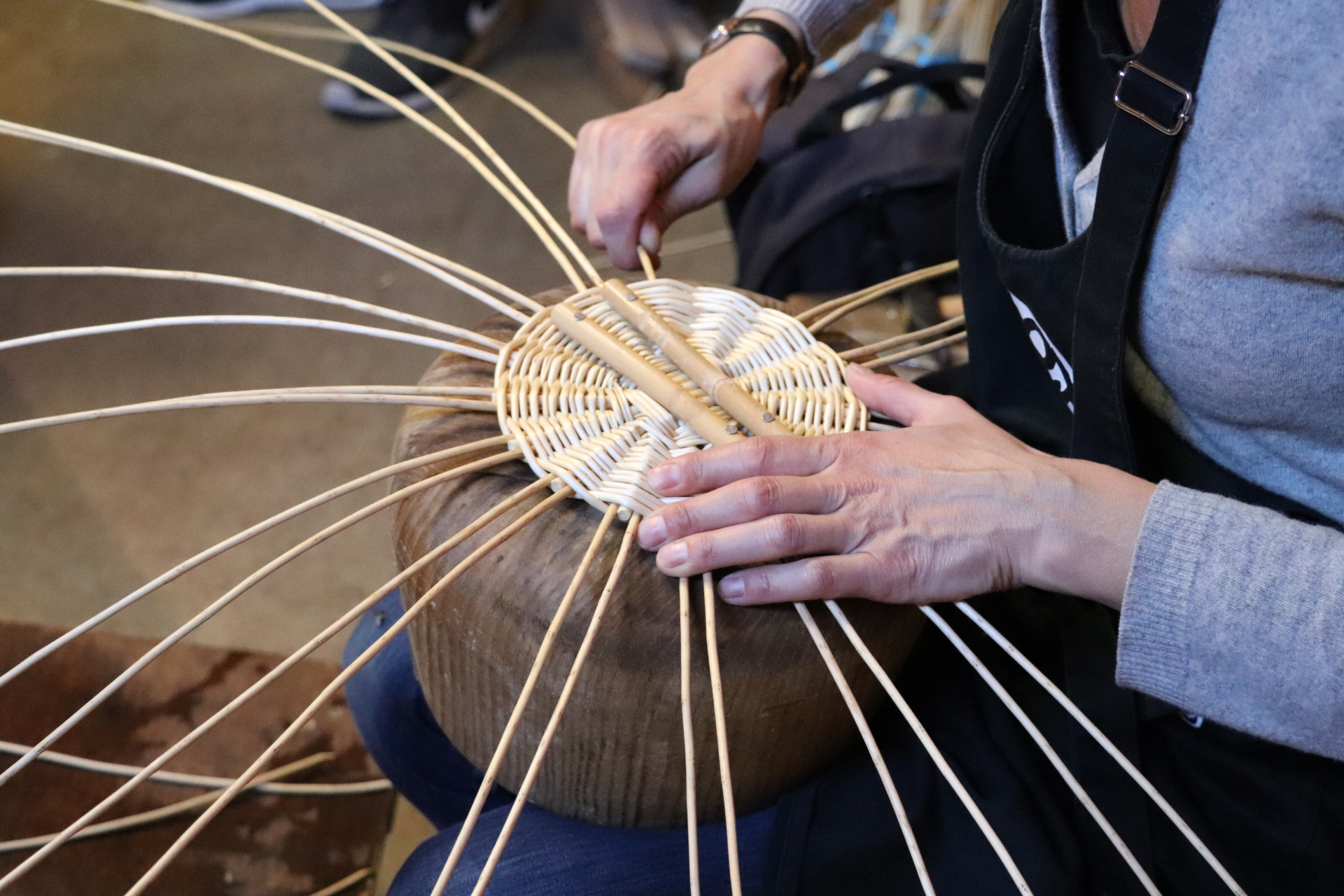
Bottom
Starting point of an object. It can be round, oval, square or rectangular and filled with twined weaving, crocane or chain pairing.
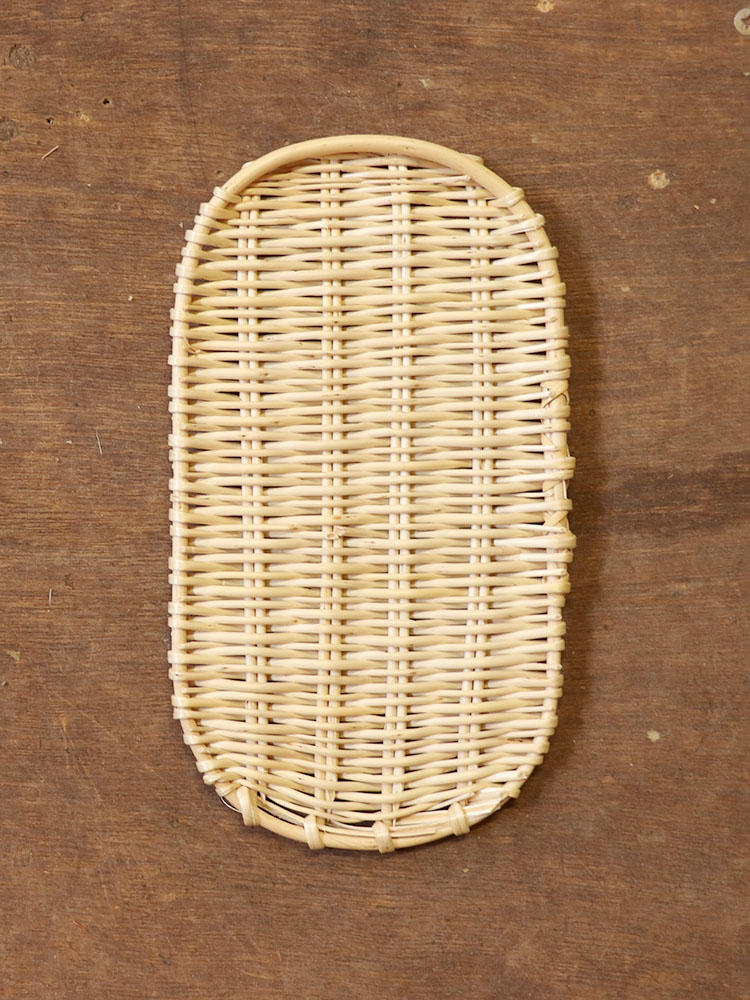
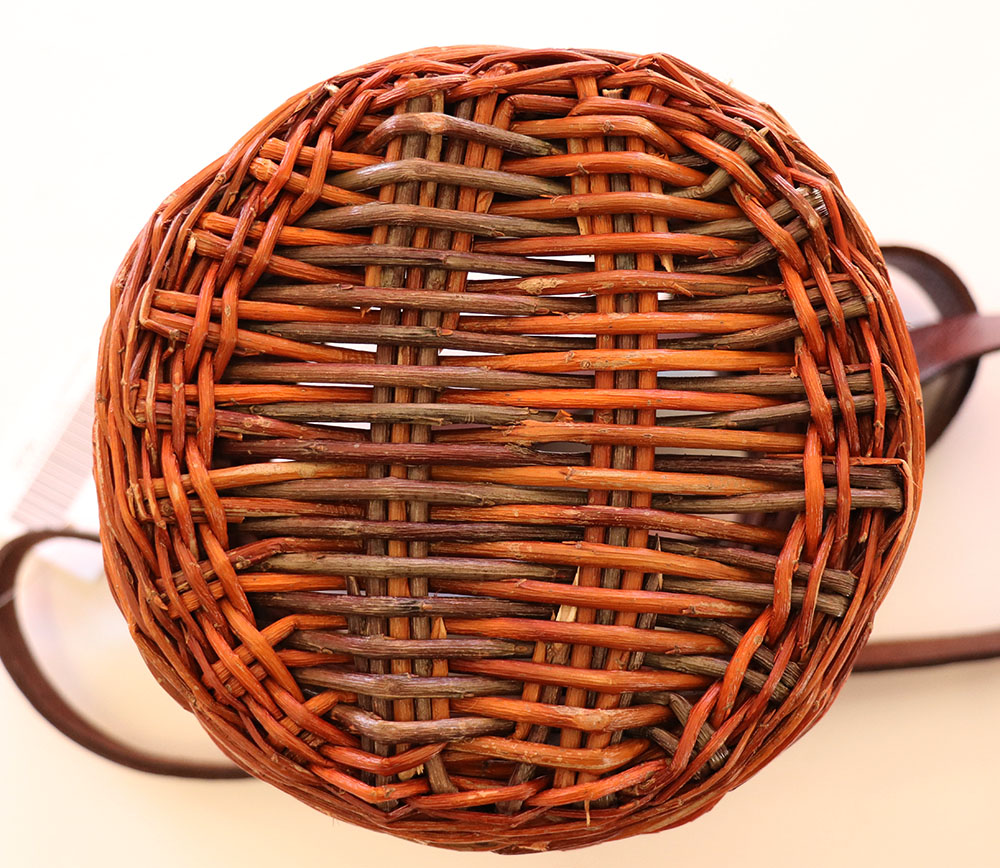
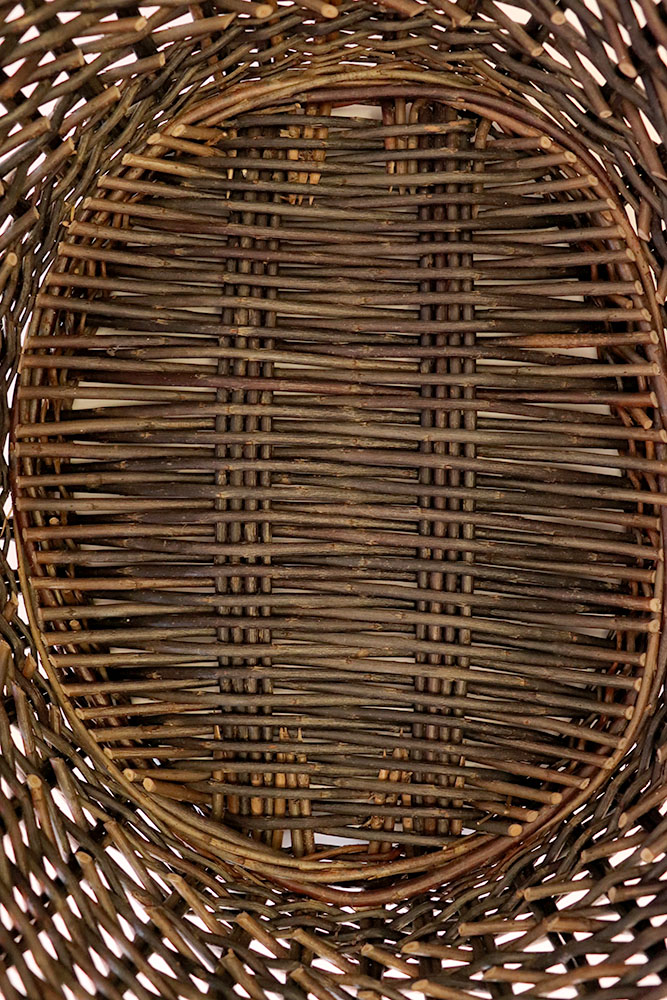





Open wicker bottom
Bottom made of very straight wicker sticks, or wooden slats, held together by traces.

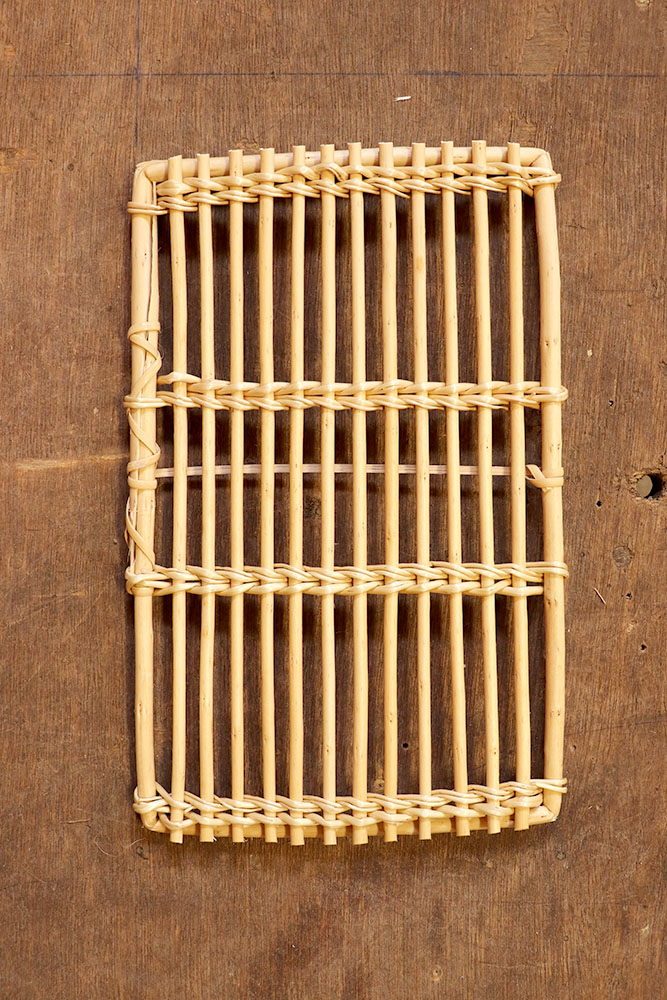

Catalan bottom
Bottom on a mould in which the strands are cut at the edge of the mould or used to make ribs.



Bottom on crosspiece
Bottom starting with three or four sticks with more sticks going through. The sticks (or spokes) are spread out as they are filled.
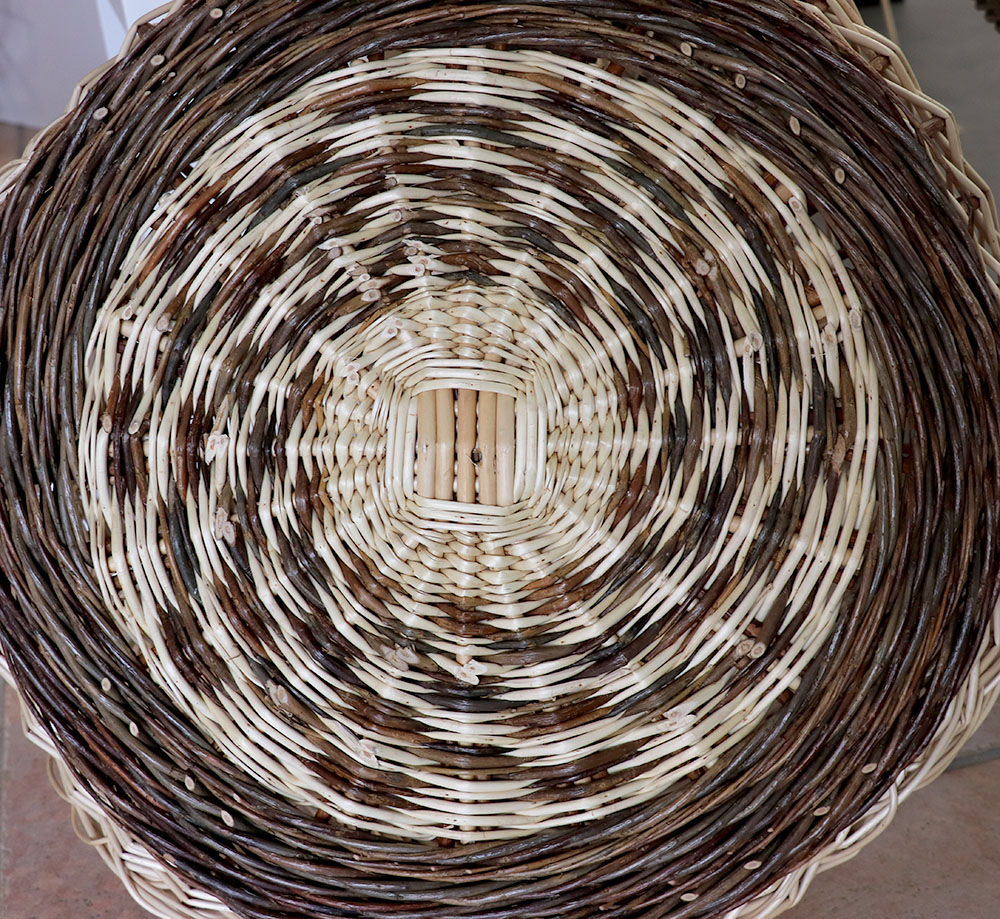





Bottom on a mould
A bottom made from a circular, oval or rectangular shape of wicker (which can be created from a template), crossed by strands hemmed onto this structure, between which one comes to fill in by weaving with twined weaving.




Hit
Wickerwork characterised by a tightly woven weave on an oak slat support (van, hood for example).


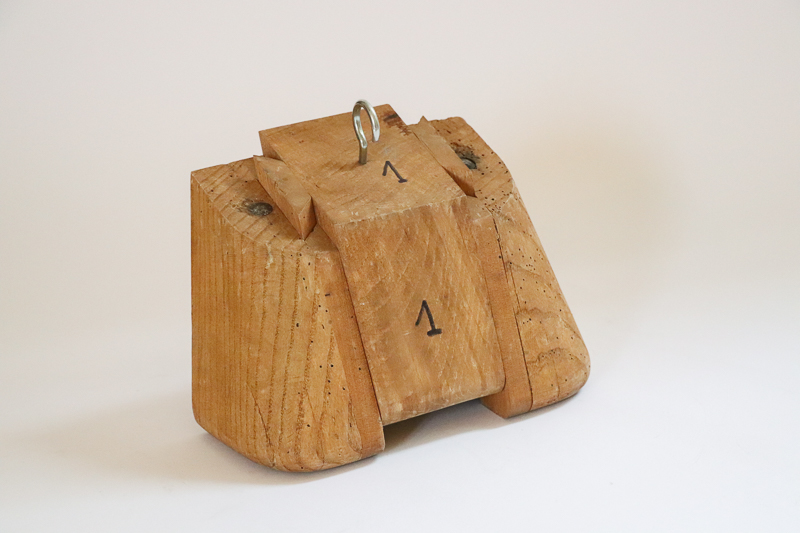
Template
Made of wood or iron, it is used to form the framework of the background or to tighten the trace work.


Rattan marrow
The inner part of the rattan vine. The vine is stripped of its bark and then mechanically calibrated to obtain stems of regular marrow. When the gauge is large, the marrow is useful for making furniture. When the gauge is small, in thin strips, it can be weaved.

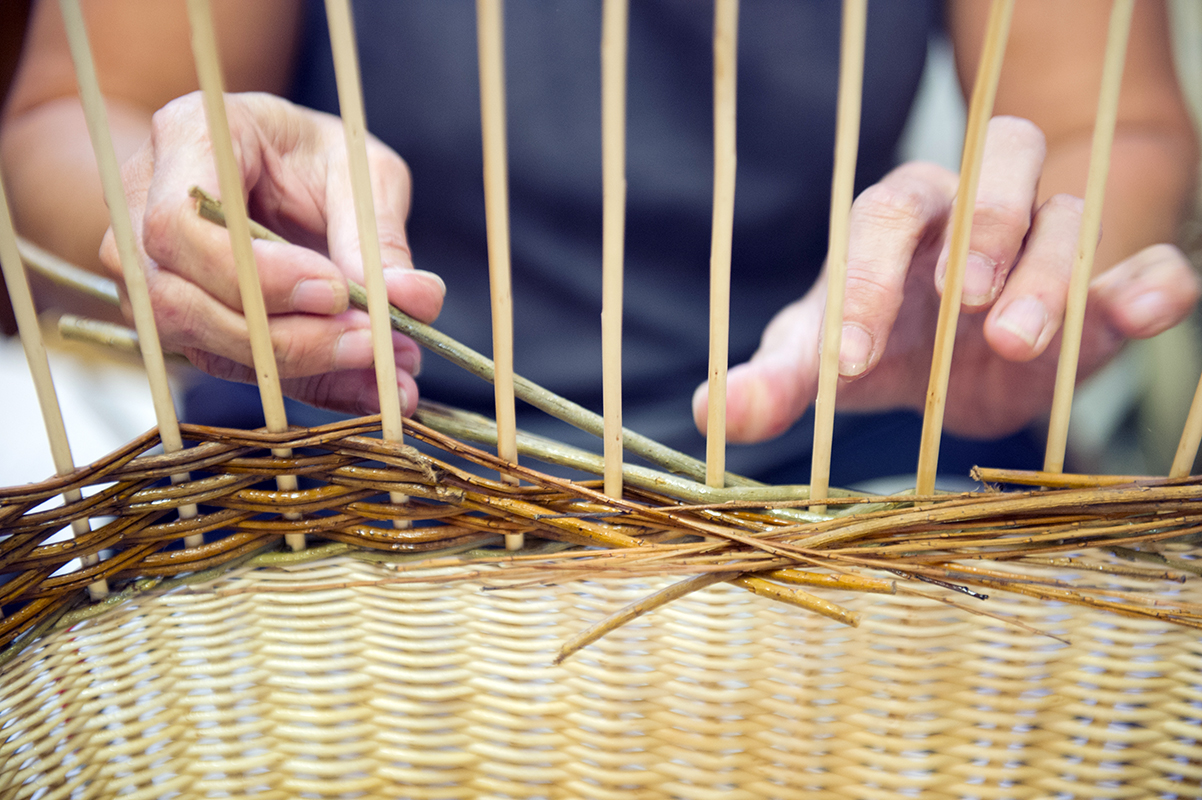
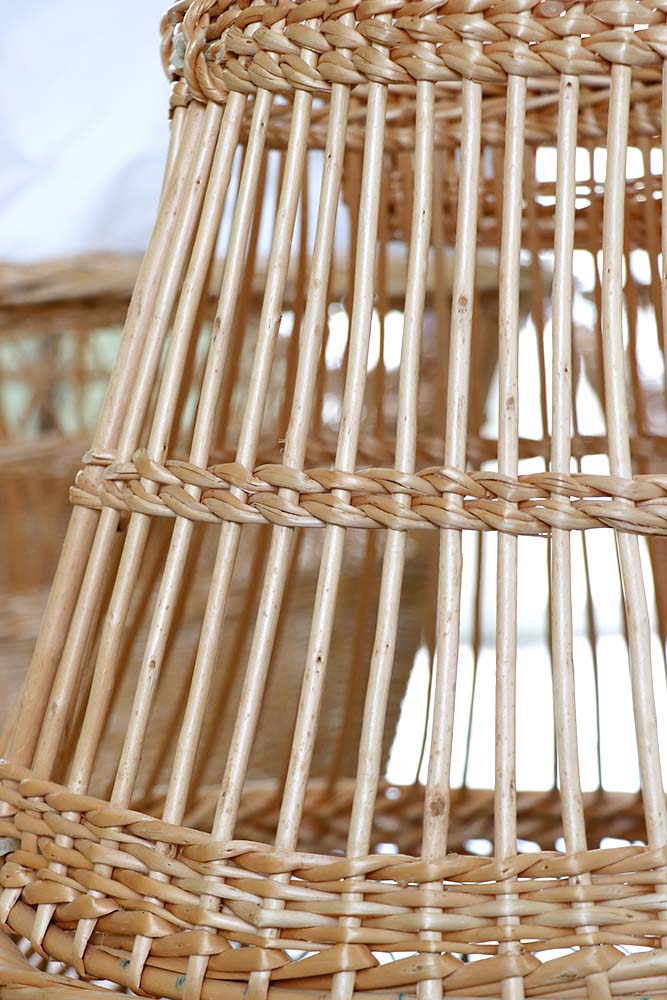
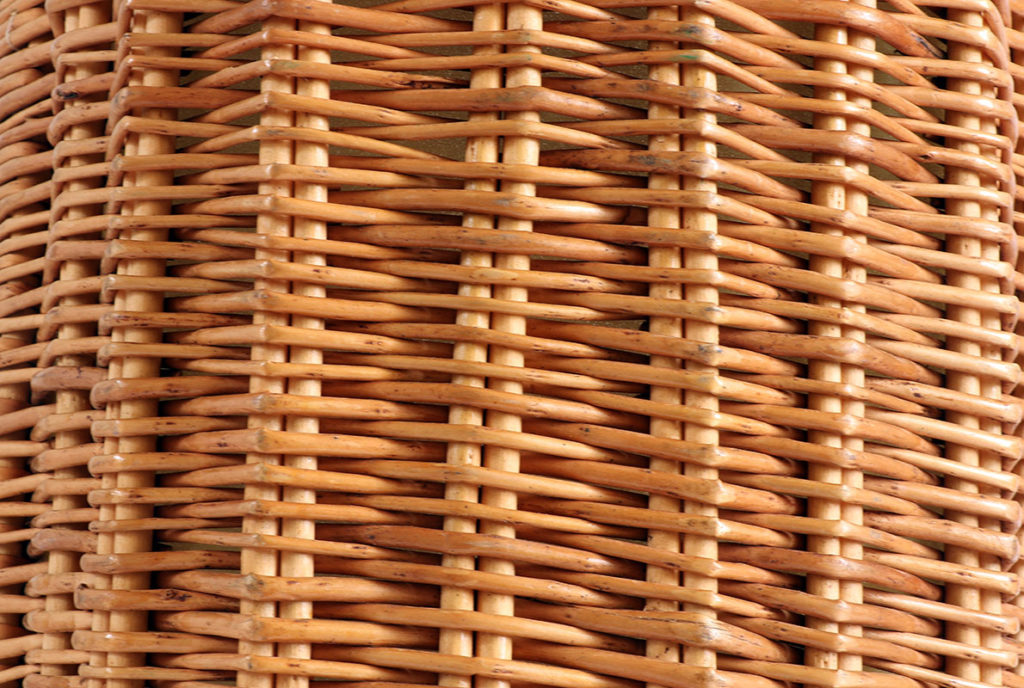
Ribs
In the body of the basket, the ribs are the strands that occupy the vertical position around which the other wicker is interwoven. They can be fixed in two ways: warped to the bottom mould or stitched into the bottom.
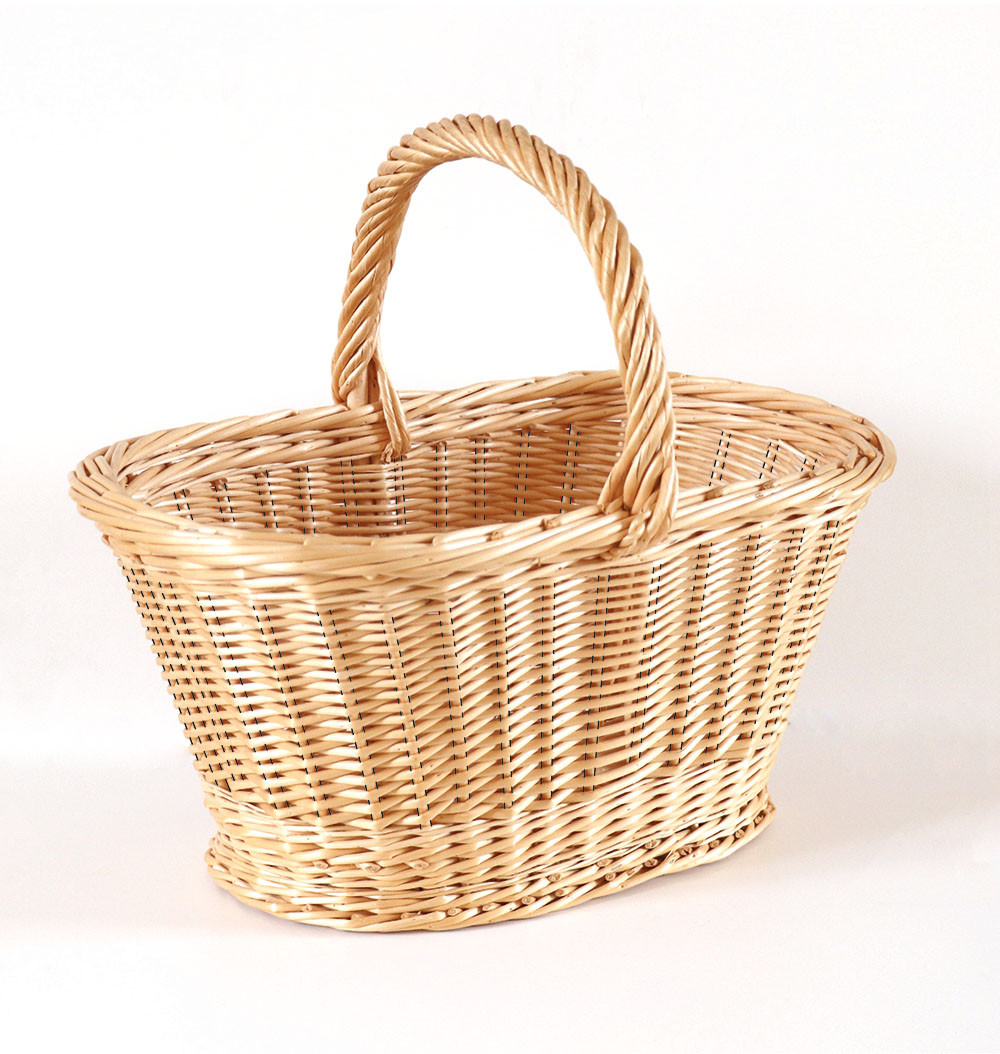


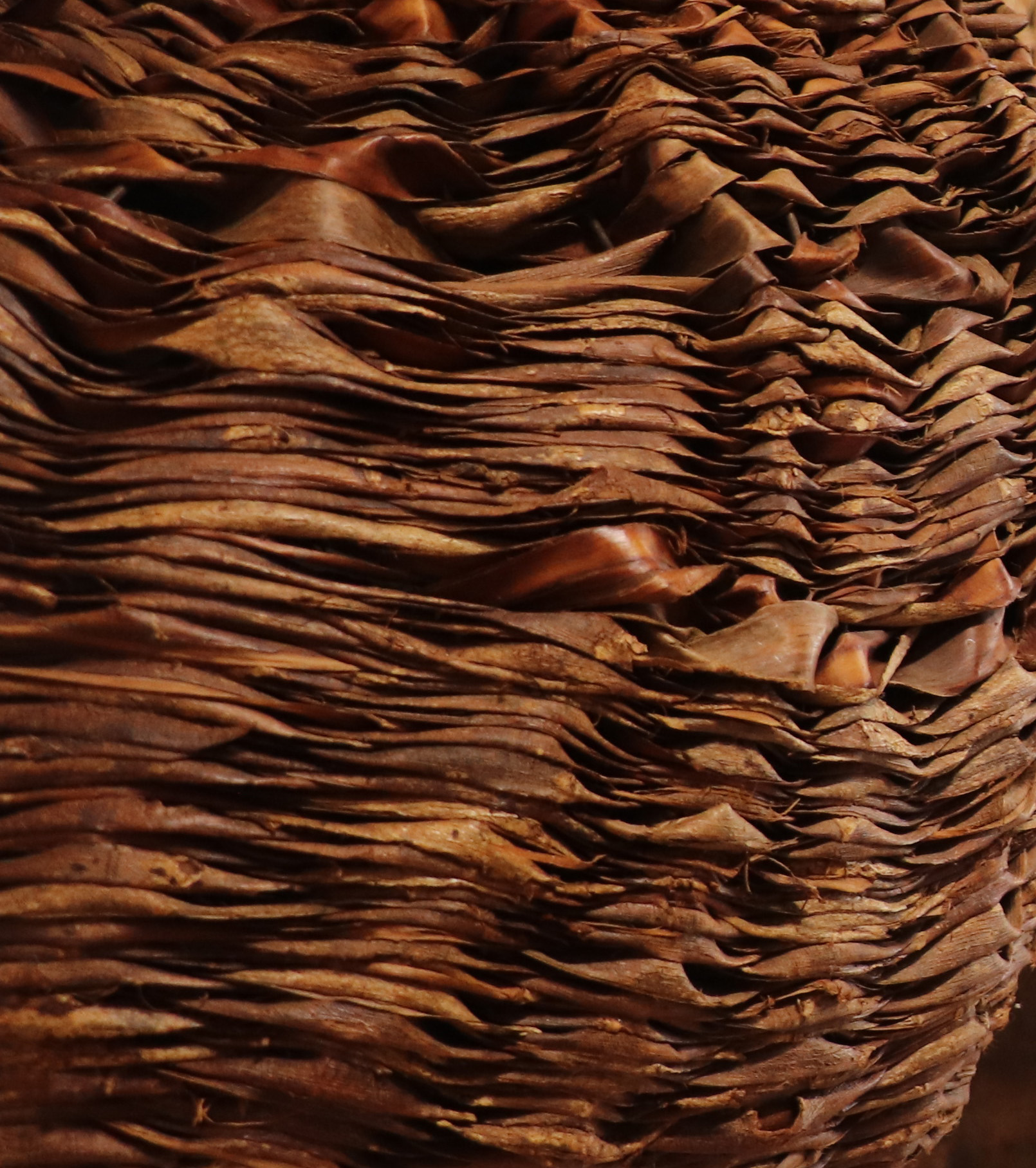
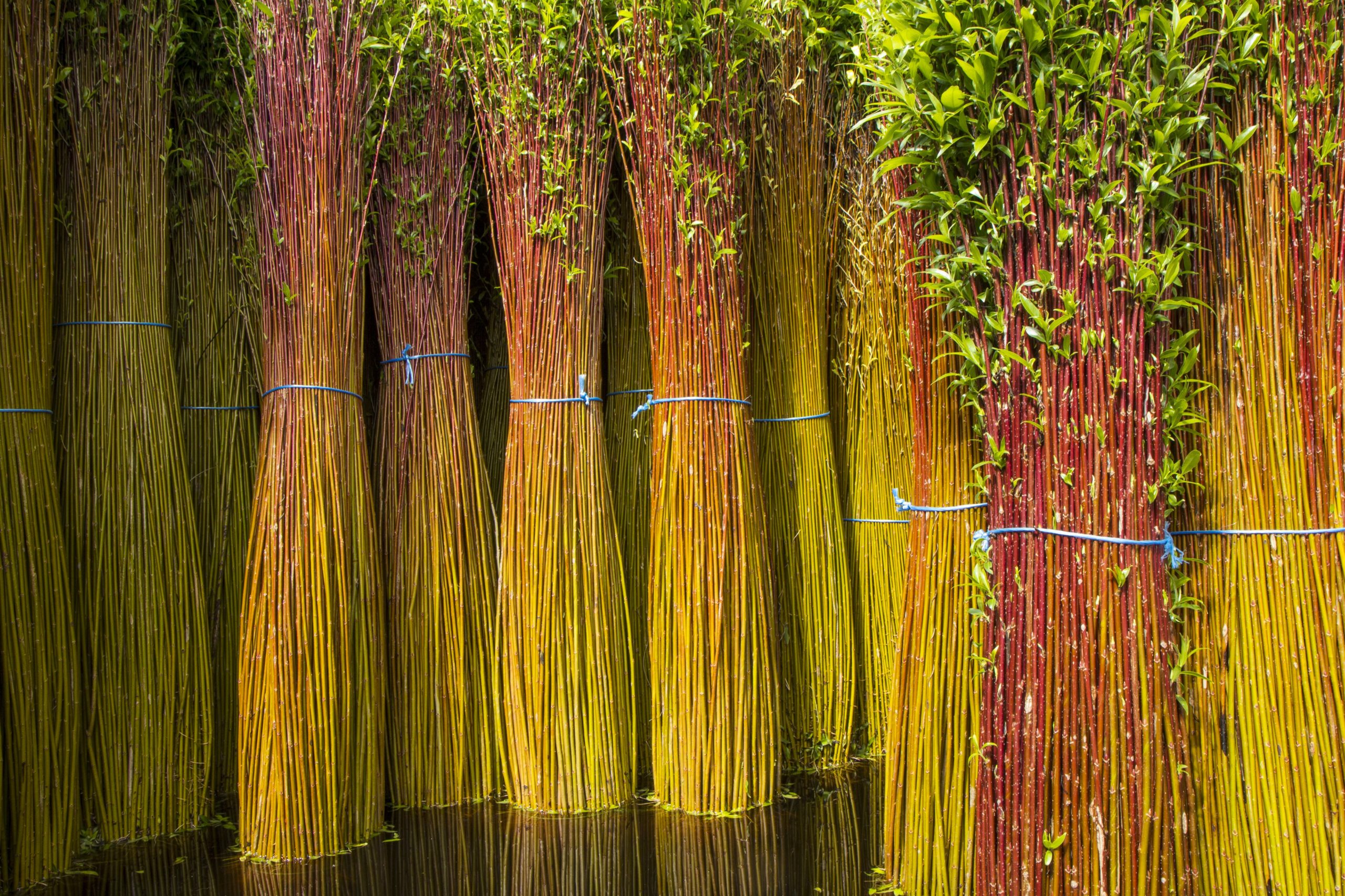
Wicker
Willow branches of the year. Harvested in winter, sorted by size, and dried to make the main plant material worked by the basket maker. Different varieties are grown for their quality and colour.
Wicker has a foot and a top that do not allow for braiding without variation in diameter.

White wicker
Osier dont l’écorce a été retirée avant séchage, ayant un aspect lisse et brillant et une couleur allant du blanc au doré.


Untrated wicker
Wicker from which the bark has not been removed before drying, having a rough appearance and a colour that can vary according to the variety (brown, red, green, yellow...)


Buff wicker
Wicker that has been boiled to remove its bark. The tannin in the bark penetrates in the strand during cooking.


Split wicker
Wicker divided into 2, 3 or 4 equal parts along its length. Manually with a splitter or mechanically with a splitting machine.

Green wicker
Freshly harvested wicker that has not been dried. It is not very suitable for manufacturing because green wicker loses half its volume during drying, which would make the basket less solid.

Hemming
Mise en place des montants écaffés autour du moule pour commencer à monter l’ouvrage. On dit que les montants sont ourdis.


End
The thickest end of a strand or, in the case of a basket, a rim added to the bottom of the basket, which is in contact with the ground. It is most often composed of a few turns of torches and a border, sometimes the same as the one made on the top of the basket, sometimes different.
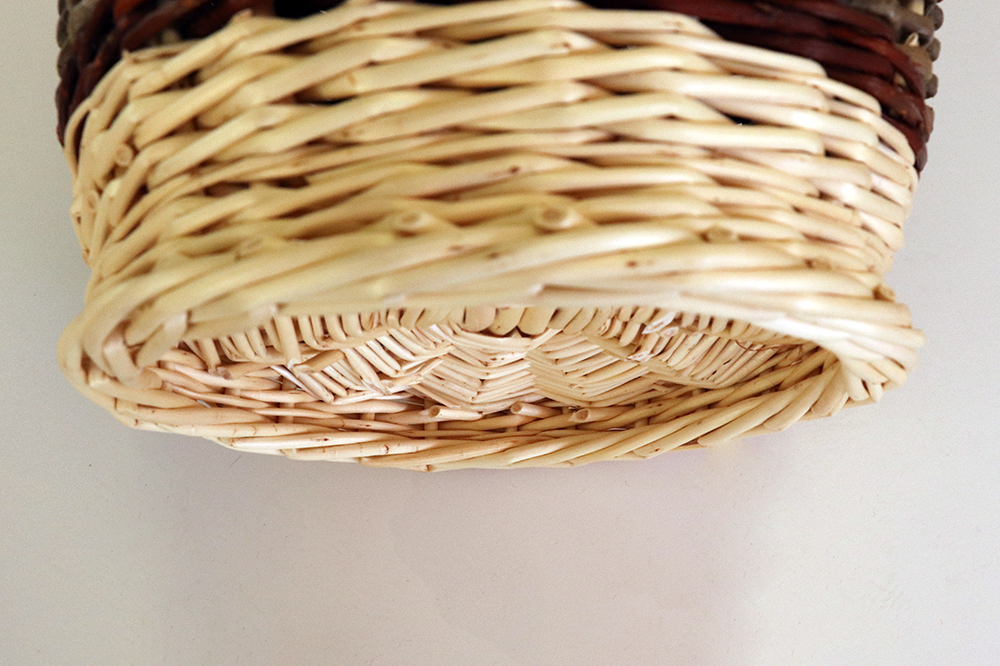




Pignon
The 'pignon' is a part of the weaving that does not go around the basket. There are many different forms.


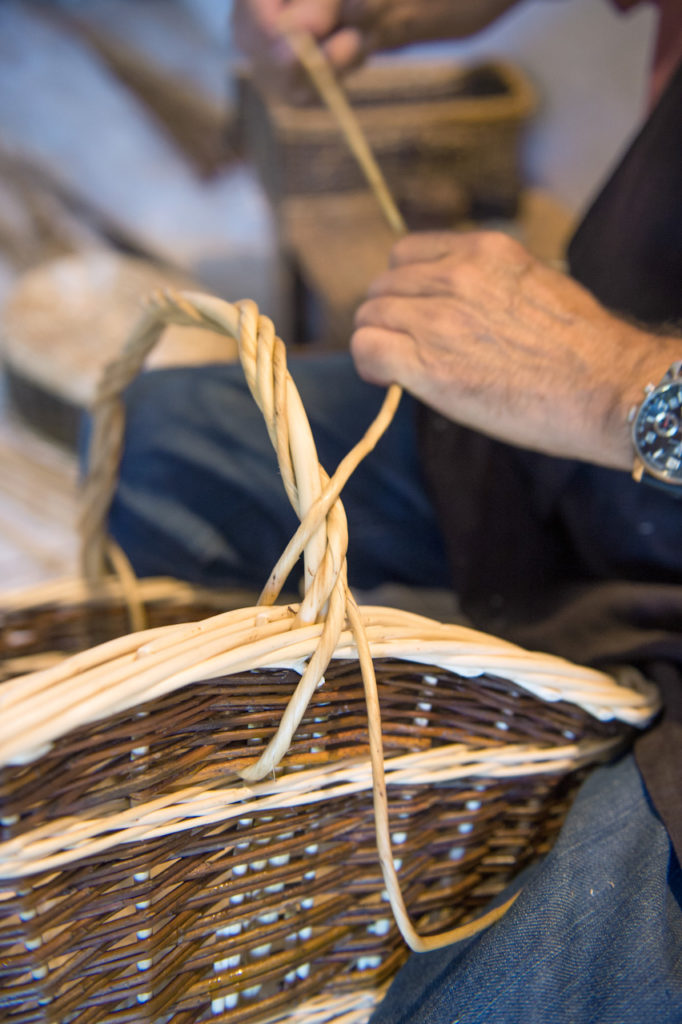
Handle strand cove
A handle made up of a single strand that strings itself, it is the simplest of the handles.

Rattan
A trailing palm tree whose stems are covered with spines. Rattan stems are long and slender and can reach up to 250 metres in length with a diameter of no more than 60 mm. It grows in the tropical forests of equatorial Africa, South America, Australia, India and South-East Asia. There are many varieties of this palm tree, only a few of which are used as raw material for furniture.

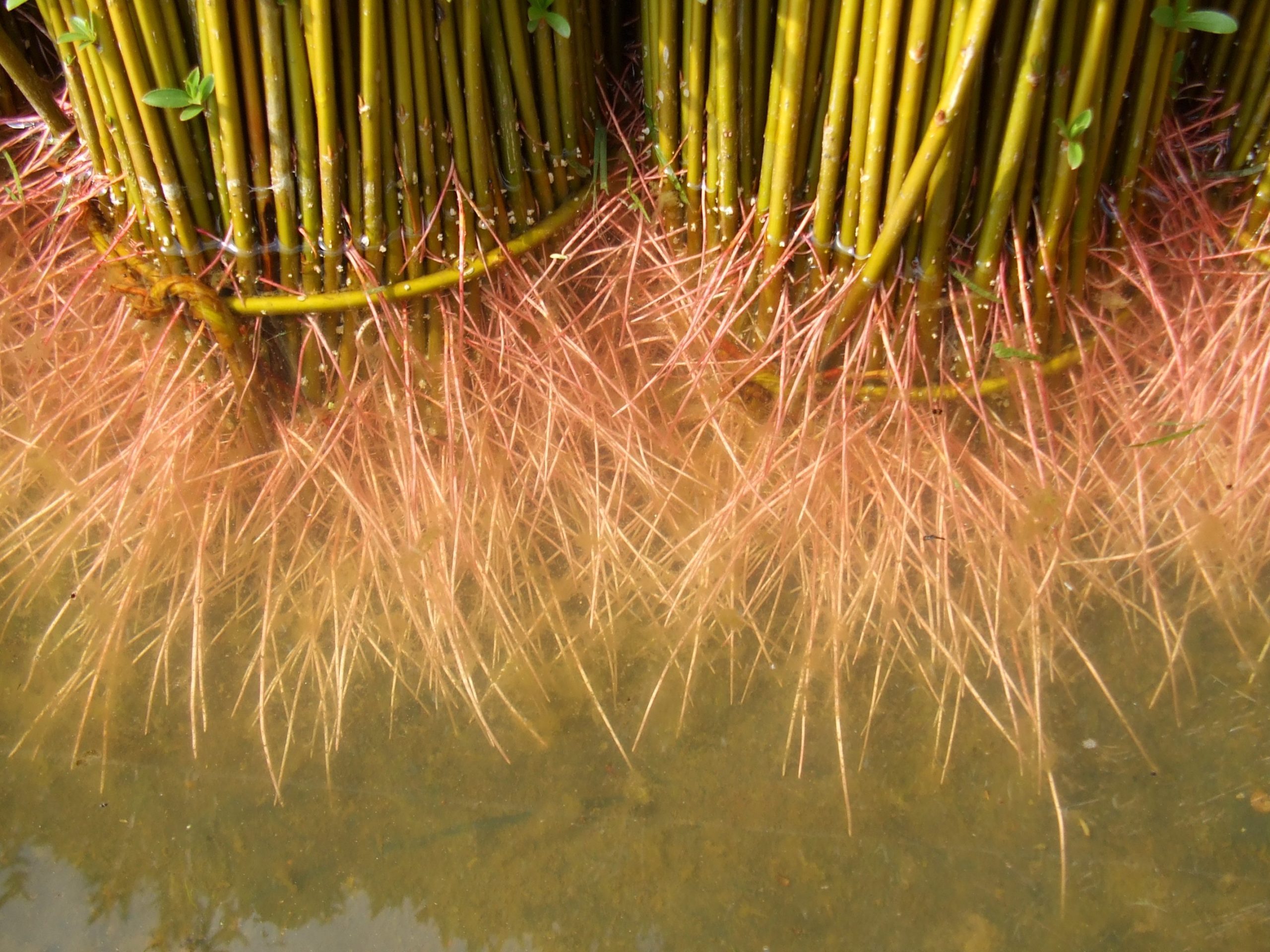
Routoir
A natural or artificial basin in which the foot of the wicker bundles, previously graded, is immersed to allow them to regenerate from winter to spring. This process allows the riseof sap in the wicker strands and makes it possible the peel's detachment at the time of debarking in the spring.



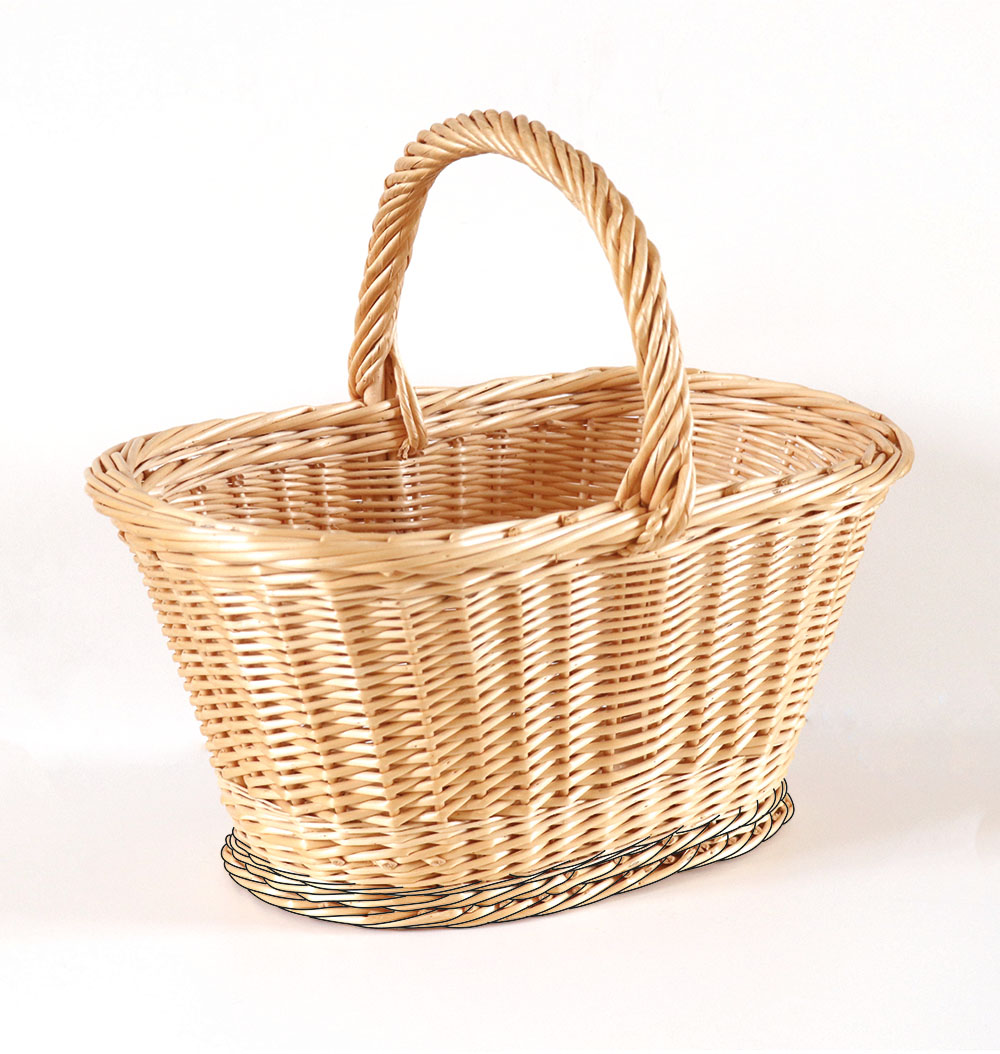
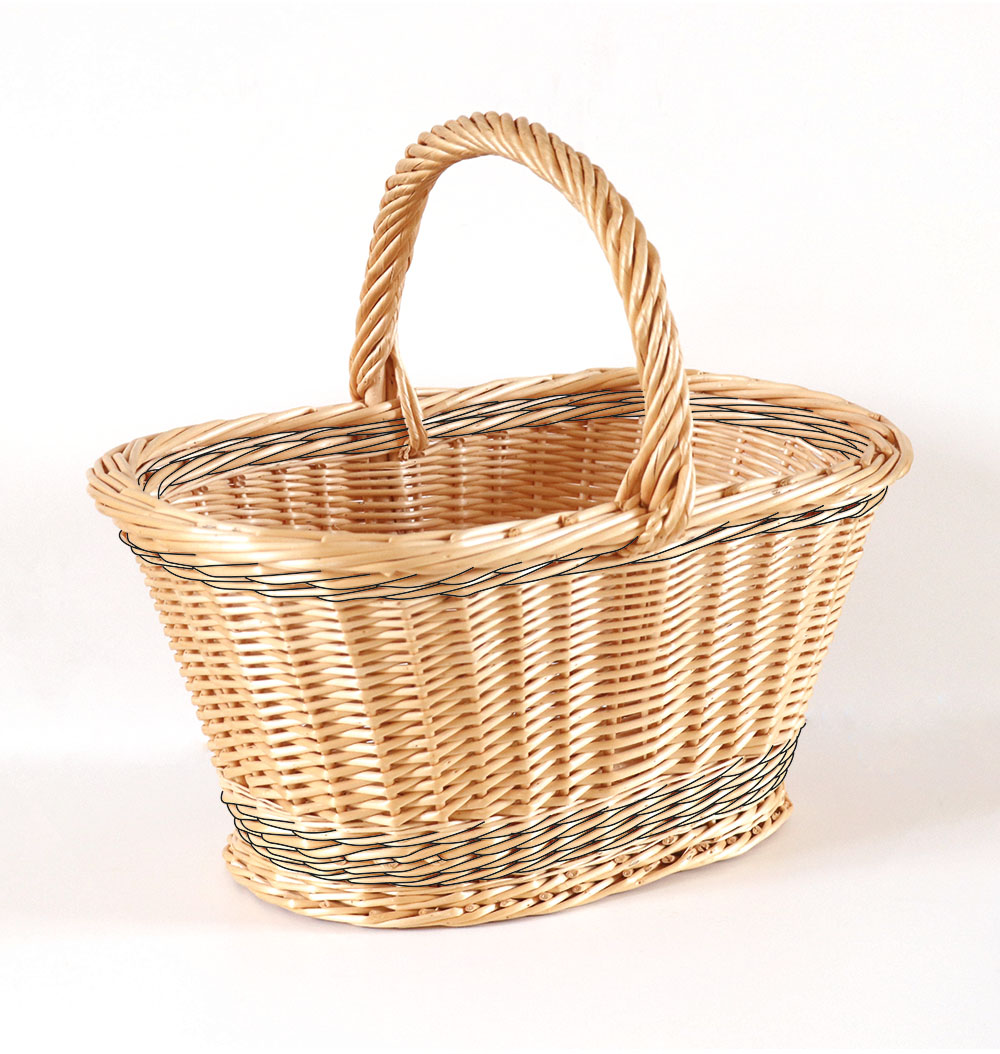
Sub Handle
Also known as "soul", it is a large strand of wicker, or more rigid wood, using as a framework on which strands of wicker or splint are wound to form the handle. This makes for a more robust handle.


Torch
Assembly at least three strands intertwined around the ribs giving the illusion of a string. It is placed before the start of a weaving to reinforce the structure or at the end of a weaving before the edge to level and maintain the weaving.


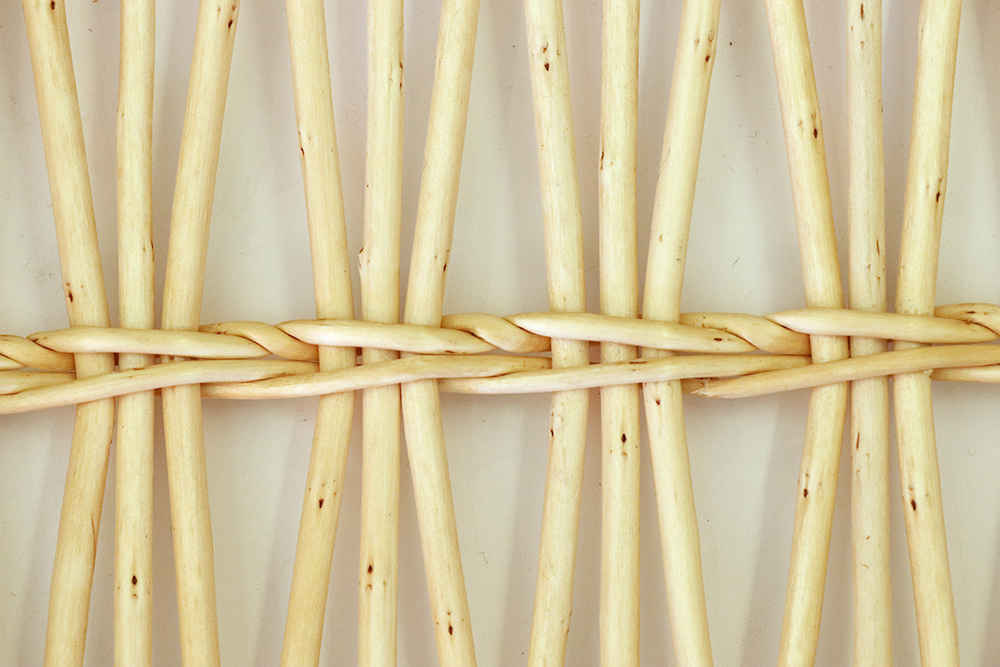
Trace
Two strands of wicker intertwined between the ribs and the coursons to keep them in the open work.

Trace mesh
A trace in which the two strands wrap around themselves between two ribs. Used to create or fill a wider distance between two ribs.
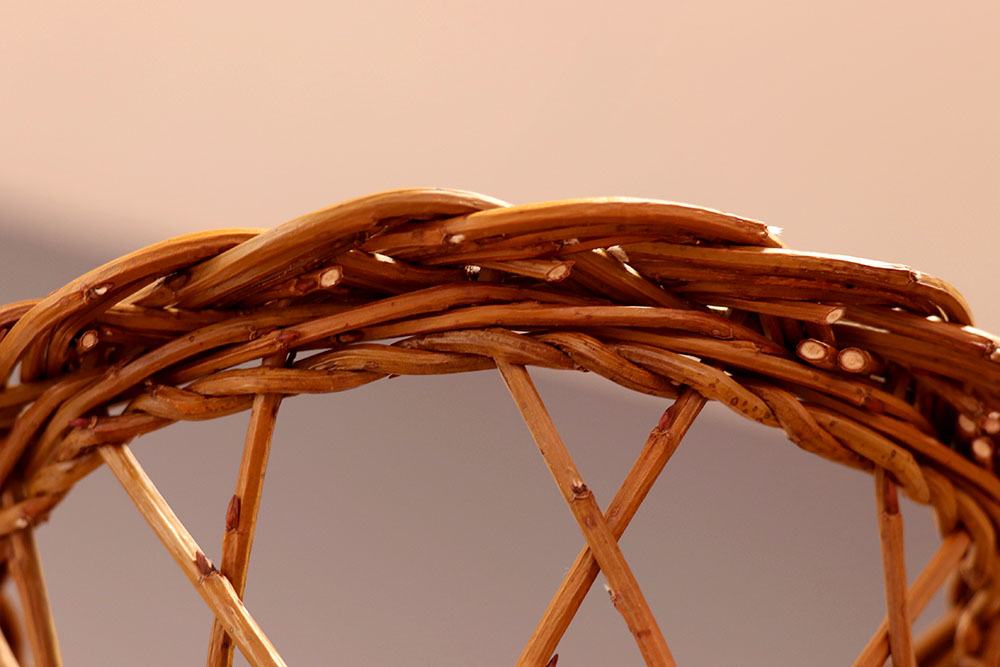



Open work
Assembly of ribs separated from each other in width by traces. The ribs are more or less close to each other, giving a more or less openwork. It is also called "openwork basketry" and "openwork weaving".

Solid work
As opposed to openwork, the term "solid work" is used for work where the walls are entirely covered with weaving. It is also known as "solid basketry" and "solid weaving".

Soaking
Process of immersing plant fibers in water before using them, in order to soften them. Step is essential for weaving wicker or rattan.

Scratch gauge
Tool for scratching the width or thickness of the wicker splint by hand. It is called a width or thickness tool.